Press Release by S5
press release materials for one dozen streams
Project maintained by s5collab Hosted on GitHub Pages — Theme by mattgraham
The materials for the press release on “Twelve for dinner: The Milky Way’s feeding habits shine a light on dark matter”
The article “S5: The Orbital and Chemical Properties of One Dozen Stellar Streams” by Ting Li and collaborators was accepted in American Astronomical Society’s Astrophysical Journal and is available here.
Links:
Images:
All the images and videos are available in high resolution to download here
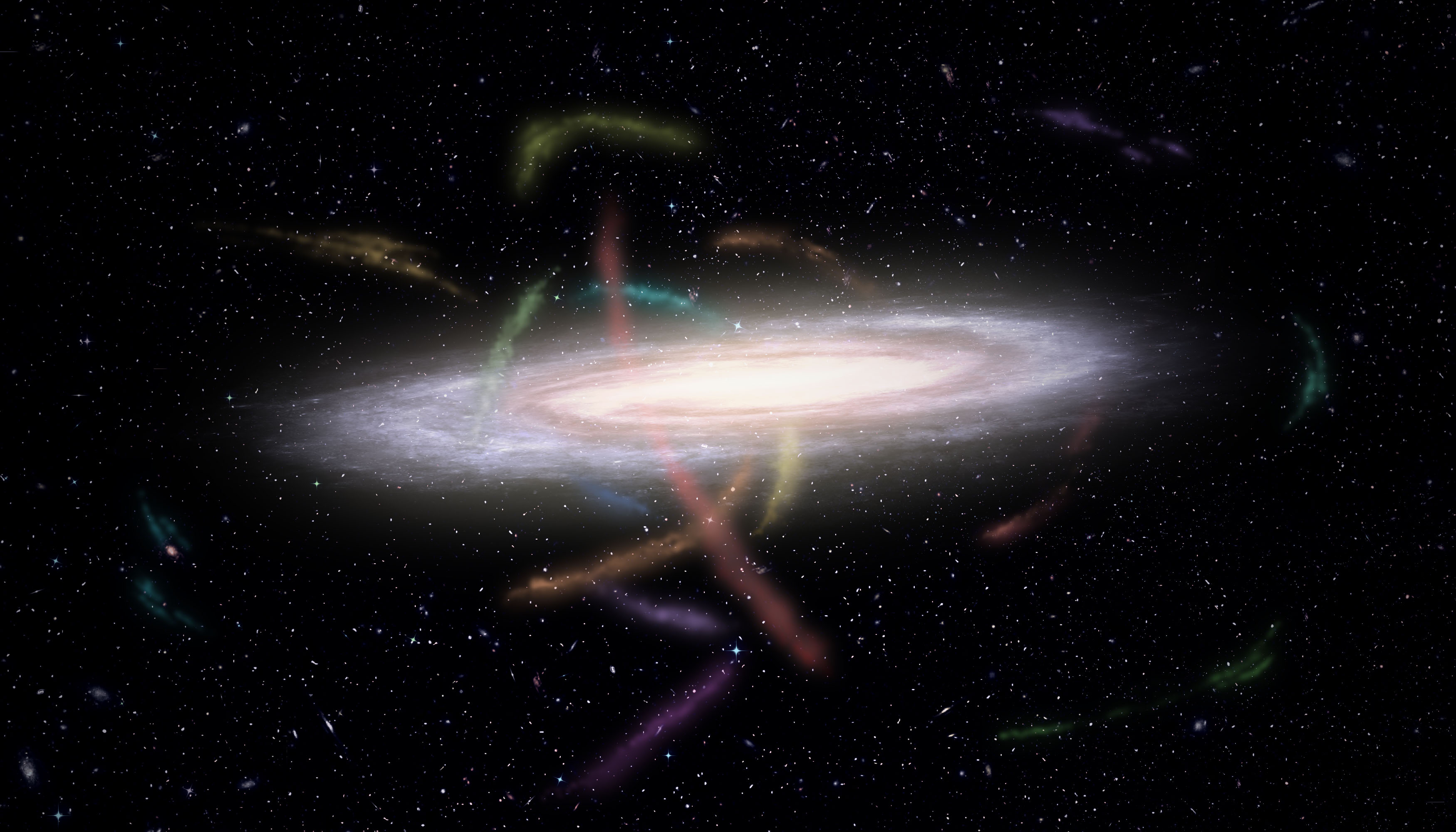 Caption: Artist’s representation of our Milky Way Galaxy surrounded by dozens of stellar streams. These streams were the companion satellite galaxies or globular clusters that are now being torn apart by our Galaxy’s gravity. (Credit: James Josephides and S5 Collaboration) Download Image
Caption: Artist’s representation of our Milky Way Galaxy surrounded by dozens of stellar streams. These streams were the companion satellite galaxies or globular clusters that are now being torn apart by our Galaxy’s gravity. (Credit: James Josephides and S5 Collaboration) Download Image
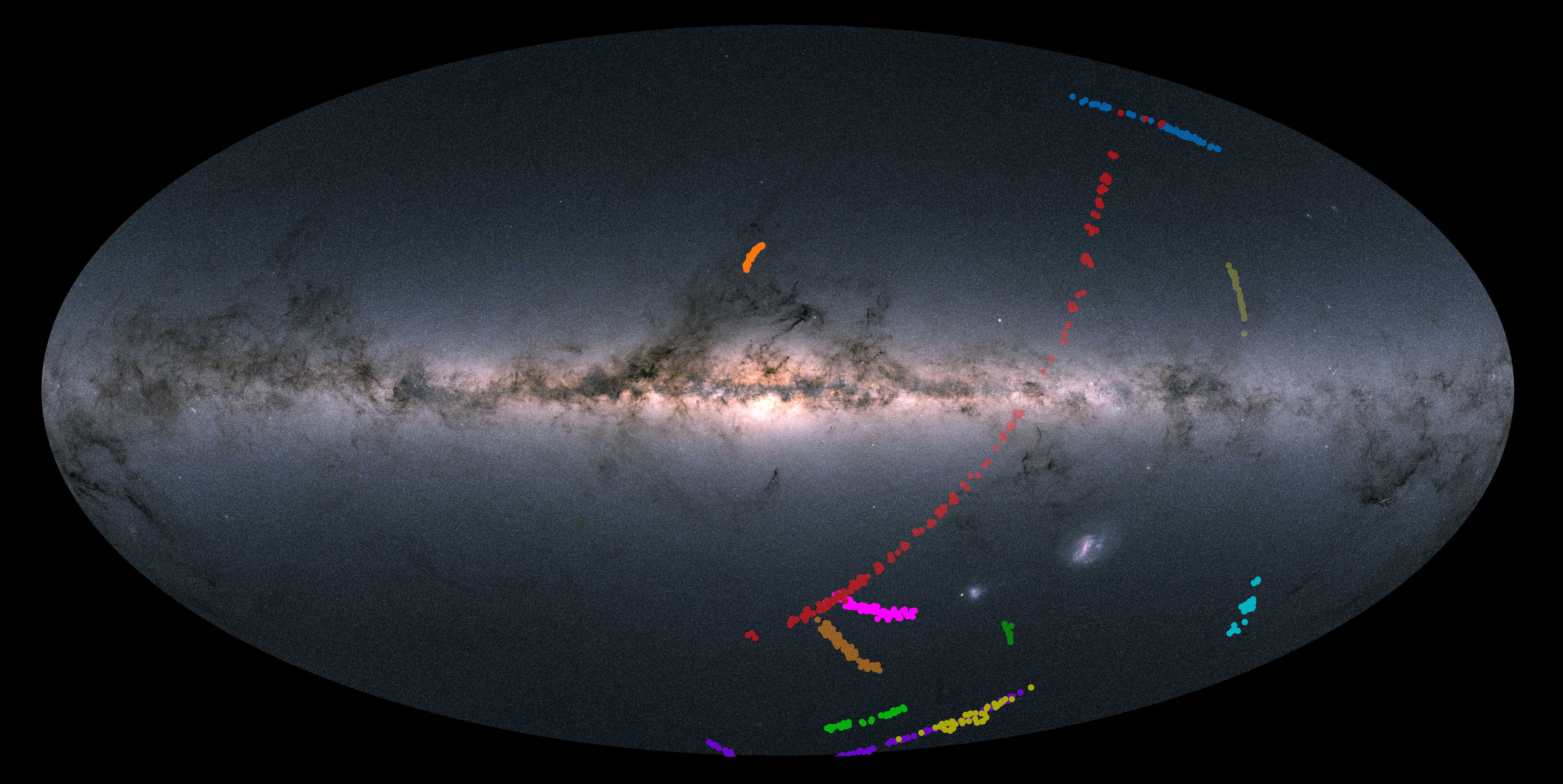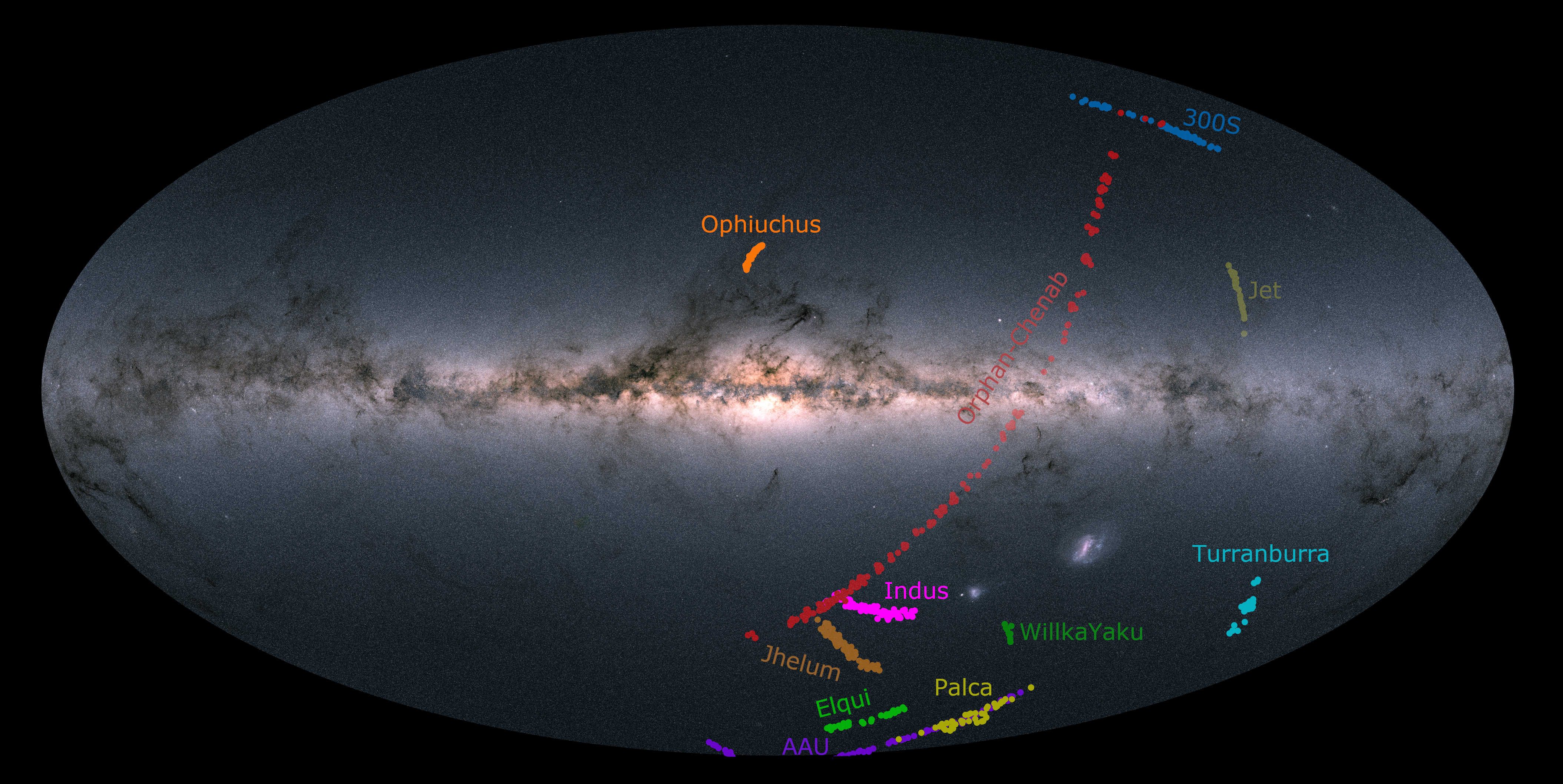
 Caption: Location of the stars in the dozen streams as seen across the sky. The background shows the stars in our Milky Way from the European Space Agency’s Gaia mission. The AAT is a Southern Hemisphere telescope so only streams in the Southern sky are observed by S5. (Credit: Ting Li, S5 Collaboration and European Space Agency)
Download Image w/ label, Download Image w/o label
Caption: Location of the stars in the dozen streams as seen across the sky. The background shows the stars in our Milky Way from the European Space Agency’s Gaia mission. The AAT is a Southern Hemisphere telescope so only streams in the Southern sky are observed by S5. (Credit: Ting Li, S5 Collaboration and European Space Agency)
Download Image w/ label, Download Image w/o label
Caption: Artist’s impression of twelve stellar streams observed by S5, seen from the Galactic South Pole. (Credit: Geraint F. Lewis, S5 Collaboration) Download Image
Videos
Caption: A movie showing the 3-D location of individual stars in the dozen streams observed by S5. The colors of individual points are according to a star’s 3-D velocity. (Credit: Sergey Koposov, S5 Collaboration) Download Video
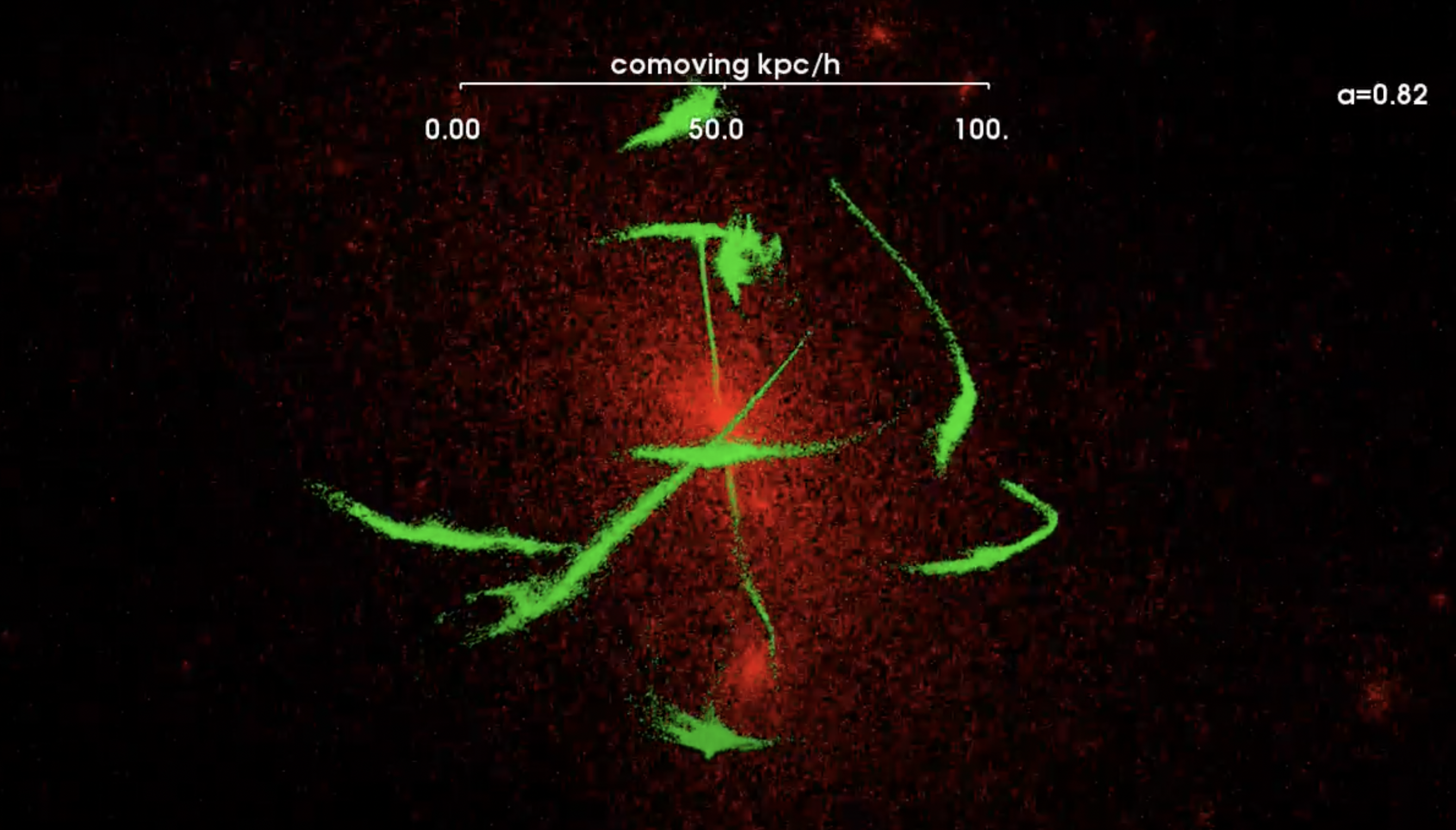
Caption: The tidal disruption of ten globular clusters in the Milky Way for 8 billion years. The red particles show the dark matter of the simulated Milky Way and the green particles show the disrupting globular clusters. The stars from the disrupting globular cluster form long stellar streams which follow the orbit. Astronomers use these streams to measure the mass distribution and clumpiness of dark matter in the Milky Way, as well as the accretion history of our Galaxy. (Credit: Denis Erkal, S5 Collaboration) Download Video
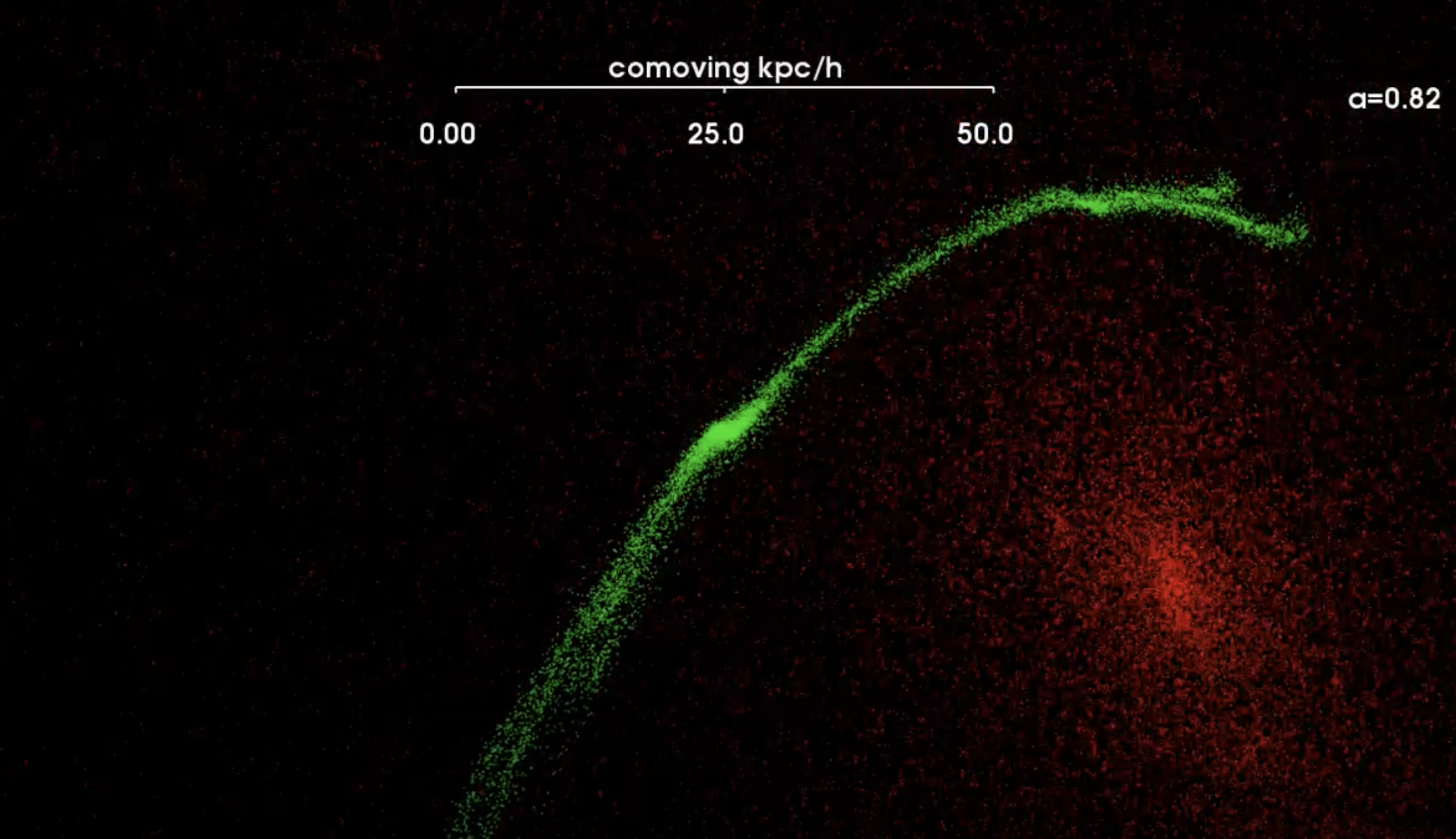
Caption: This follows one globular cluster being torn into a tidal stream over 8 billion years. The red particles show the dark matter of a large galaxy and the green particles show a disrupting globular cluster. The stars near the progenitor form a characteristic “S”-shape due to the gravitational influence of the globular cluster. (Credit: Denis Erkal, S5 Collaboration) Download Video